Table of Contents
Humanized antibodies are antibodies produced in non-human animals. Humanized antibodies on production, if injected into humans, can cause damage due to variation in protein structure. These are altered earlier to become humanized.
The Necessity of Humanized Antibodies
Drugs are toxic substances and are effective when used in the appropriate dosage. However, due to the development of resistance, there is a demand for increasing dosage that is toxic to humans. Most of the therapeutic agents are ineffective in treating various diseases.
In replacement for these therapeutic agents, antibodies are demanded. Among these antibodies, monoclonal antibodies are the best solution for passive immunity. These humanized antibodies direly need to be produced for increasing human demands.
The Role of Mouse Models in Humanized Antibodies
Humanized antibodies are best to be generated in mouse models due to genetic similarities between humans and mice. For example, monoclonal antibodies obtained from mice exhibit very little variation from human antibodies compared to antibodies originating from other animals.
Different Methods of Making Mouse Models
Sometimes lymphocytes of humans are fused with Epstein Barr virus or myeloma cells of the mouse to produce humanized antibodies. But under few circumstances, the hybrid cells lose human chromosomes and become unstable. The effective ways to produce humanized antibodies are:
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA technology is mainly used to produce humanized antibodies. The target gene involved in antibody coding is isolated and cloned in cells, mainly mouse cells. These mouse cells will act as antibodies-producing factories. The target gene insertion and deletion in the mouse genome required alterations to produce the desired sequence of amino acids in antibodies.

Chimeric Intermediate
The antibody (Fc) producing gene segment fused with the mouse antibody Fab portion to produce monoclonal antibodies in humans. Such fusion is described as a human-mouse chimera. Mainly FC portion of the mouse antibody is replaced with the human antibody Fc portion for humanization.
The production of chimera selectively replaced the mouse antibody Fc portion with the human Fc portion. The amino acid sequences of the human Fc portion are altered by using genomic alterations tools. In chimera, selective alterations are made in the Fab portion of the mouse that varies from the Fab portion. The selective alterations are carried out in a way to maintain the integrity and specificity of antibodies. The CDR region of the mouse Fab portion is never altered for selective binding of antibodies with target cells.
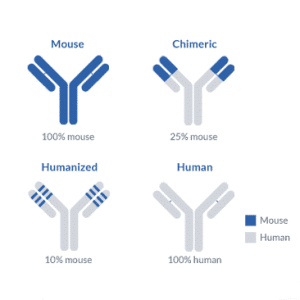
Insertion of Relevant CDRs
The recombinant DNA technology can be used to produce humanized antibodies without intervening in the chimeric intermediates. Following the production of antibodies in the non-human system, the DNA encoding antibody may be sequenced, and the CDR region of antibodies will be determined. Now, a strategy can be developed to produce such CDR DNA sequence-based fragments along with antibody production. The linear DNA sequences are needed for this purpose.
The Value of Humanized Antibodies Techniques
- CDR grafting
The complementarity determining regions (CDR) are hypervariable regions of antibodies and are responsible for the specific binding of antibodies with the target. A humanization technique is CDR grafting, in which the CDRs of parental antibodies are carefully selected and grafted into the human framework to produce humanized antibody sequences.
- Phage Display Technologies
In phage display technology, DNA-protein, protein-protein, and peptide-peptide interactions are studied through bacteriophage. Further, a connection is generated in a protein molecule and gene-encoded. The epitope mapping is conducted, and ligands are isolated from phage libraries. These are useful for drug design, validation of therapeutic efficacy of drugs, and development of a vaccine. In addition, the phage display technology is used for the strategic applications of humanized antibodies in clinical cases as therapeutic measures.
- Transgenic Mice
The mouse-generated humanized antibodies as a therapeutic agent have been impaired due to the inherent immunogenicity of these molecules. The production of monoclonal antibodies with very low inherent immunogenicity involves the use of transgenic mice. The transgenic mice express repertoires for human antibody gene sequences. Transgenic mice originated humanized antibodies exhibit high specificity and efficacy compared to others.
Conclusion
Cyagen provides humanized antibodies for research and commercialization point of view and is also providing the best transgenic mice model to produce highly specific humanized antibodies.



